Income Tax Deductions List: Deductions on Section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD & 80D - FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25)
The Income Tax Department, recognizing the significance of fostering savings and investments, has incorporated a comprehensive set of deductions under Chapter VI A of the Income Tax Act. While Section 80C stands out as a widely known provision, several other deductions exist, providing taxpayers with opportunities to strategically reduce their tax liabilities. These deductions serve as powerful incentives, allowing individuals to optimize their financial planning and contribute to the nation’s economic growth.Let us understand these deductions in detail:
In this guide, we will explain to you all the income tax deductions of the Income Tax. Let’s get started!
Contents
# What is Income Tax Deduction under Chapter VI A of Income Tax Act?
# Section 80 Deduction List – Who can Claim Income Tax Deductions?
# Investments that Qualify for Deductions under Section 80C
# Expenses that Qualify for Tax Deductions under Section 80C
# Features of Income Tax Deduction u/s 80
# Frequently Asked Questions
What is Income Tax Deduction under Chapter VI A of Income Tax Act?
Income Tax Deduction under Chapter VIA of Income Tax Act refers to a reduction in the taxable income of an individual or a business entity, which results in a lower tax liability. The Indian Income Tax Act provides for various deductions under different sections, which can be claimed by an individual or a business entity while calculating their taxable income.
Let us take an example of tax saving for individuals with yearly salaries up to 20 lakhs.
Tax saving calculation for yearly income-20 lakhs
| Gross Salary | 2,000,000 |
| Less: | |
| HRA | 200,000 |
| LTA | 40,000 |
| Reimbursements | 24,500 |
| Children education and hostel allowance | 9,600 |
| Standard Deduction | 50,000 |
| Professional Tax | 2400 |
| Taxable Salary Income | |
| Less: Deductions | |
| 80C (Refer Note below) | 150,000 |
| 80D | 50,000 |
| 80E | 22,000 |
| Net Taxable Income | 14,51,500 |
| Tax on the above income | 2,57,868 |
| Rebate u/s 87A | Not applicable |
| Total Tax | 2,57,868 |
| Apart from this, you can also claim these tax deductions if eligible: | |
| Interest on home loan EMIs under Section 24b | -2,00,000 |
| Principal amount of the home loan under section 80EEA | -1,50,000 |
| National Pension Scheme (NPS) investments u/s 80CCD(1B) | -50,000 |
Section 80 Deduction List - Who can Claim Income Tax Deductions??
Only eligible taxpayers can claim these deductions in their income tax returns. Such eligible taxpayers have been specified under various sections of the Act. In some cases, it is individual, in some it is companies, HUF, etc. It is pertinent to note that the taxpayers who opt to pay tax under the new tax regime can claim only deductions under sections 80CCD(2) and 80JJAA.
Income tax deduction needs to be claimed at the time of filing your Income Tax Return, and no separate disclosure compliances are required for claiming such deductions. The number of deductions should be reduced from the gross income to reach the taxable amount.
| Sections | Income Tax Deduction for FY 2023-24(AY 2024-25) | Eligible person | Maximum deduction available for FY 2023-24(AY 2024-25) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section 80C | Investing into very common and popular investment options like LIC, PPF, Sukanya Samriddhi Account, Mutual Funds, FD, child tuition fee, ULIP, etc | Individual Or HUF | Upto Rs 1,50,000 |
| Section 80CCC | Investment in Pension Funds | Individuals | |
| Section 80CCD (1) | Atal Pension Yojana and National Pension Scheme Contribution | Individuals | |
| Section 80CCD(1B) | Atal Pension Yojana and National Pension SchemeContribution (additional deduction) | Individuals | Upto Rs 50,000 |
| Section 80CCD(2) | National Pension SchemeContribution by Employer | Individuals | Amount Contributed or 14% of Basic Salary + Dearness Allowance (in case the employer is Government) 10% of Basic Salary+ Dearness Allowance(in case of any other employer) – Whichever is lower |
| Section 80D | Medical Insurance Premium, preventive health checkup and Medical Expenditure | Individual Or HUF | Upto Rs 1,00,000 |
| Section 80DD | Medical Treatment of a Dependent with Disability | Individual Or HUF | Normal Disability (atleast 40% or more but less than 80%): Rs 75000/- Severe Disability (atleast 80% or more) : Rs 125000/- |
| Section 80DDB | Interest paid on Loan taken for Higher Education | Individuals | No limit (Any amount of interest paid on education loan)upto 8 assessment years |
| Section 80EE | Interest paid on Housing Loan | Individuals | Upto Rs 50,000 subject to some conditions |
| Section 80EEA | Interest Paid on Housing Loan | Individuals | Upto Rs 1,50,000/- subject to some conditions |
| Section 80EEB | Interest paid on Electric Vehicle Loan | Individuals | Upto Rs 1,50,000 subject to some conditions |
| Section 80G | Donation to specified funds/institutions. Institutions | All Assessee (Individual, HUF, Company, etc) | 100% or 50% of the Donated amount or Qualifying limit, Allowed donation in cash upto Rs.2000/- |
| Section 80GG | Income Tax Deduction for House Rent Paid | Individual | Rs. 5000 per month 25% of Adjusted Total Income Rent paid – 10% of Adjusted Total Income – whichever is lower |
| Section 80GGA | Donation to Scientific Research & Rural Development | All assessees except those who have an income (or loss) from a business and/or a profession | 100% of the amount donated. Allowed donation in cash upto Rs.10,000/- |
| Section 80GGB | Contribution to Political Parties | Companies | 100% of the amount contributed No deduction available for the contribution made in cash |
| Section 80GGC | Individuals on contribution to Political Parties | Individual HUF AOP BOI Firm | 100% of the amount contributed. No deduction available for the contribution made in cash |
| Section 80RRB | Royalty on Patents | Individuals (Indian citizen or foreign citizen being resident in India) | Rs.3,00,000/- Or Specified Income – whichever is lower |
| Section 80QQB | Royalty Income of Authors | Individuals (Indian citizen or foreign citizen being resident in India) | Rs.3,00,000/- Or Specified Income – whichever is lower |
| Section 80TTA | Interest earned on Savings Accounts | Individual Or HUF (except senior citizen) | Upto Rs 10,000/- |
| Section 80TTB | Interest Income earned on deposits(Savings/ FDs) | Individual (60 yrs or above) | Upto Rs 50,000/- |
| Section 80U | Disabled Individuals | Individuals | Normal Disability: Rs. 75,000/- Severe Disability: Rs. 1,25,000/- |
Investments that Qualify for Deductions under Section 80C
Tax saving options under Section 80C
There are several options you can choose to save tax under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. These include:
- 1. Equity Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS)
- 2. National Pension Scheme (NPS)
- 3. Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP)
- 4. Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- 5. Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY)
- 6. National Savings Certificate (NSC)
- 7. Fixed Deposit (FD)
- 8. Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
Please note that these benefits are available if you have chosen the “Old Tax Regime.”
Expenses that Qualify for Tax Deductions under Section 80C
Life Insurance Premiums
Employee Provident Fund (EPF) contributions
Public Provident Fund (PPF) investments
National Savings Certificate (NSC) investments
Equity-Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS) investments
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) investments
5-Year Fixed Deposit with Banks
Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS) investments
Tuition Fees for up to two children
Home Loan Principal Repayment
Stamp Duty and Registration Charges for a Home
Features of Income Tax Deduction u/s 80
Section 80C: This section provides a deduction of up to Rs. 1.5 lakh for investments in specified instruments such as EPF, PPF, NSC, ELSS, tax-saving fixed deposits, etc.
A list of other investments that are eligible for deduction under section 80C. is enumerated below
- 1) Premium paid for life insurance policy Premium paid on insurance policies of self, spouse, or child (minor or major). If you pay a premium for your parents, then you will not be allowed to take a deduction. If In the case of HUF, the premium paid for any member. It can be either a life policy or an endowment policy.
- 2) Any amount invested in the Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme in the name of your daughter or any girl child for whom you are a legal guardian.
- 3) Contribution to:
– Public Provident Fund
– Approved superannuation fund
– Unit-linked Insurance Plan, 1971
– Unit-linked Insurance Plan of LIC Mutual Fund
– Approved annuity plan of LIC
– Pension fund which is set up by mutual fund or by the administrator or the specified company
– National Housing Bank Term Deposit Scheme, 2008
– additional account under NPS
– Senior Citizens Savings Scheme Rules, 2004 - 4) Subscription to::
– National Savings Certificates (VIII issues)
– units of any mutual fund or from the administrator or the specified company
– notified deposit scheme of a public sector company that provides long-term finance for construction or purchase or construction of houses for residential purposes in India or any other deposit scheme concerned with housing accommodation or planning, improvement or development of cities, towns, and villages or both.
– specified equity shares or debentures or units of mutual fund
– notified bonds issued by NABARD - 5) Investment in five-year fixed deposit (FD) of Scheduled Bank or Post Office
- 6) Repayment of housing loan principal amount(including stamp duty, registration fee, and other expenses)
- 7) Payment of tuition fees to any college, school, university or other educational institutions within India for full-time education for maximum 2 children
Section 80CCC: This section provides a deduction for contributions made to annuity plans of LIC or any other insurer for receiving pension.
Under section 80CCC income tax deduction for the contributions made in specified pension plans can be claimed. The tax deduction can be claimed by individuals (whether resident or non-resident). Maximum permissible deduction under sections 80C, 80CCC, and 80CCD(1) put together is Rs. 1,50,000
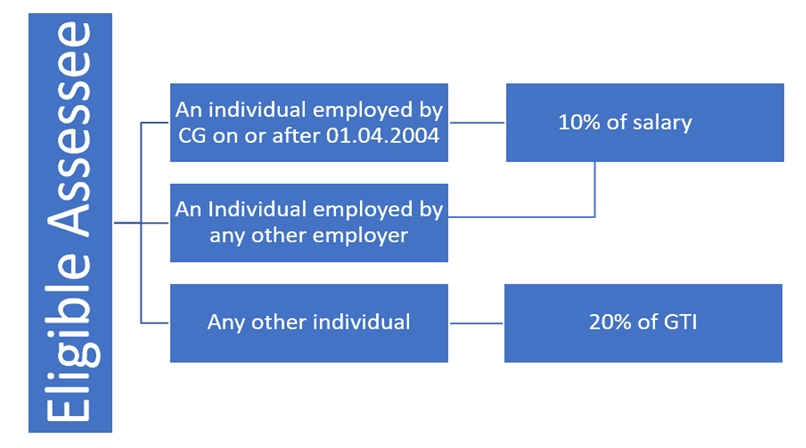
Section 80CCD(1): An income tax deduction for contributions made by individuals to eligible NPS
The contribution made to eligible NPS account is tax-deductible up to Rs 1.5 lakhs under section 80CCD(1). The deductions shall be restricted to the amount contributed or the below-given percentage, whichever is less. However, this tax benefit is within the overall ceiling limits of section 80CCE, i.e., Rs. 1,50,000. To know the computation of the exempt amount, eligibility, and much more.
Section 80CCD(1B): Additional Income tax deduction for contributions made by Individual to eligible NPS
Section 80CCD(1B) gives you the additional tax saving benefit of upto Rs 50,000 for contributions to the NPS account. It is over and above the limits of section 80C,i.e. It shall not be subjected to the ceiling limit of Rs. 1,50,000. This section 80CCD has gained so much attention as you can invest up to Rs. 2 lakh in an NPS account and claim a deduction of the full amount, i.e. Rs. 1.50 lakh under Sec 80CCD(1) and Rs. 50,000 under Section 80CCD(1B). Click to know more.
Section 80CCD(2): Income tax deduction for contributions by an employer to eligible NPS
Your contribution to NPS is deductible under 80CCD(1), and 80CCD(1B), and the amount contributed by your employer towards your NPS account is also tax-deductible under section 80CCD(2). Read to know more details. The deduction amount shall be restricted to 14% of salary(Basic salary + DA) in case of central Govt. employees and 10% in case of any other employees.
Section 80D: Income Tax benefit for medical insurance premium
Section 80D is amongst the most popular tax saving options. Under this tax benefit is admissible for
1. Medical Insurance Premiums
2. Expenditure on Preventive Health Check-up
3. Other Medical Expenditure
The admissible deductions under this section are as under:
In the case of an individual
- 1. Case I – If your self / spouse or dependent children are below 60 Years of age, then the maximum deduction is Rs. 25,000, and if your parents are also below 60 years of age, then the maximum deduction is Rs. 25,000. Therefore, the aggregate deduction shall be a maximum of Rs. 50,000.
- 2. Case II – If your self / spouse or dependent children are below 60 Years of age, then the maximum deduction is Rs. 25,000, and if parents are 60 years or above, then the maximum deduction is Rs. 50,000. Therefore, the aggregate deduction shall be a maximum of Rs. 75,000.
- 3. Case III – If your self / spouse or dependent children are 60 years or above, then the maximum deduction is Rs. 50,000, and if your parents are also 60 years or above, then the maximum deduction is Rs. 50,000. Therefore, the aggregate deduction shall be a maximum of Rs. 1,00,000.
- 4. Deduction upto Rs. 5,000 shall be allowed in respect of payment made towards preventive health check-up of self, spouse, dependant children or dependant parents made during the previous year. However, the said deduction of Rs. 5,000 shall be within the overall limit of Rs. 25,000 or Rs. 50,000, specified above.
In the case of HUF
The maximum deduction available to a HUF in respect of premium paid to insure the health of any member of the family would be Rs. 25,000, and in case any member is a senior citizen, then Rs. 50,000.
Notes:
- 1. You can also claim a deduction of upto Rs. 50,000 under section 80D even if you do not have any health insurance policy provided any amount is incurred towards: – medical treatment expenditure of self, spouse and dependent children (who is of the age of sixty years or more and not having medical insurance cover) – medical treatment expenditure of any parent(s) (who is of the age of sixty years or more and not having medical insurance cover)
- 2. Deduction where the health insurance premium is paid in lump sum: Deduction shall be apportioned towards all the years for which the premium is paid.
Section 80DD: Income Tax Deduction for Medical Treatment of a Dependent with Disability
Section 80DD provides an income tax benefit to the extent of Rs 75,000 (Where disability is 40% or more but less than 80%) & Rs 1,25,000 (Where there is severe disability (disability is 80% or more) respectively. The benefit can be availed for incurring medical expenditures for a disabled dependent relative. For diseases covered, documents required and other information, please refer to the detailed guide.
Section 80DDB: Income Tax Deduction for Specified Diseases
The income tax deduction under section 80DDB serves as financial help for those suffering from a severe disease or are taking care of such dependent family members. The deduction is allowed in respect of the amount actually paid for the medical treatment of such disease or ailment of the specified persons. The maximum deduction is summarized hereunder:
| Dependant | Maximum limit (Rs.) |
| A senior citizen (being a resident individual) | 1,00,000 |
| Other than a senior citizen | 40,000 |
No such deduction shall be allowed unless a prescription is obtained for such medical treatment from a neurologist, oncologist, urologist, haematologist, immunologist, or other specialists, as may be prescribed. Read more to know the eligibility and other qualifying criteria.
Section 80E: Income Tax Deduction for Interest paid on Higher Education Loan
The interest paid on higher education loan taken for self, spouse, child or student of whom you are a legal guardian is eligible for income tax deduction under section 80E. The tax benefit is available for the 8 Assessment Years. i.e., The current year and the next 7 years, without any maximum limits.
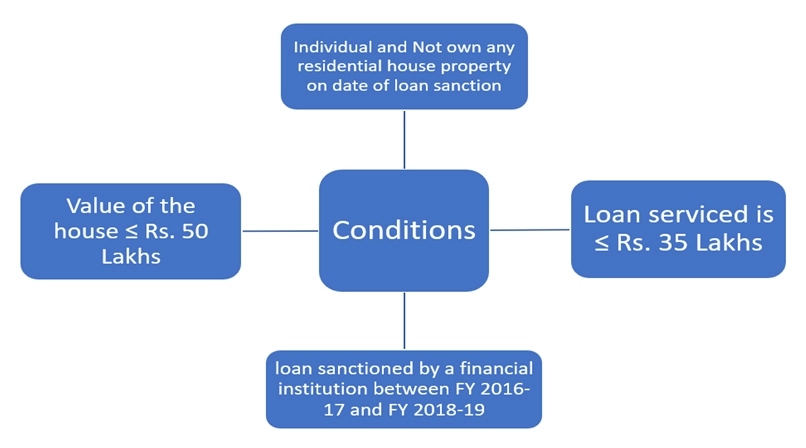
Section 80EE: Income Tax Deduction for Home Loan
Section 80EE provides an additional deduction of upto Rs. 50,000 in respect of the interest on loan taken by an individual to acquire residential house property from any financial institution. Read insights here. 80EE deduction is in addition to the deduction available under section 24 while computing ‘income from house property’. The conditions for availing deduction of interest are: here.
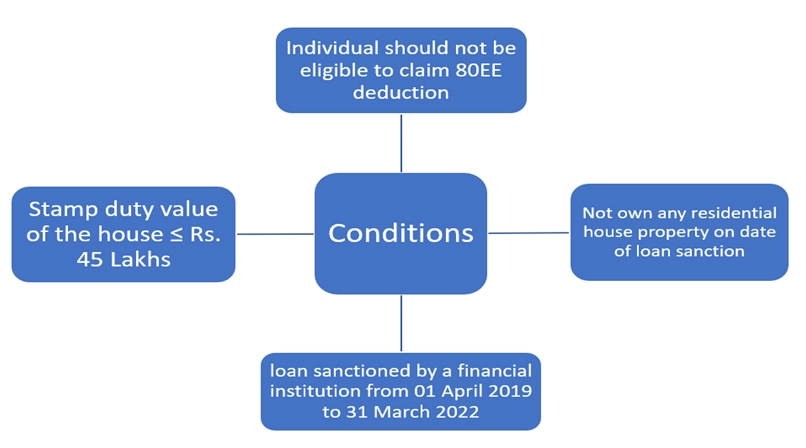
Section 80EEA: Income Tax Deduction for first time home buyers
This section is Section 80EEA which allows an additional deduction to taxpayers for paying interest on a home loan availed by them. While Section 24 allowed for interest exemption on home loans up to INR 2 lakhs, this section allows an additional exemption of Rs 1.5 lakhs to home buyers who avail a home loan and pay interest on the loan.
Other conditions for availing deduction of interest:
Section 80EEB: Income Tax Deduction for repayment of Electronic Vehicle Loan
This section was introduced to promote the purchase of electric vehicles among individuals by giving them tax relief on the interest paid on loan taken to purchase such vehicles from any financial institution from 01/04/2019 to 31/03/2023. The limit of deduction is up to Rs 1.5 lakhs.
Section 80G: Deduction in respect of donations made to specified funds and charitable institutions etc
- Deduction under this section is available to all types of taxpayers (individual/ firm/ LLP or any other person).
- The deduction amount is based on the category in which the fund falls, i.e. with or without any qualifying limit. Where the funds are subject to qualifying limit, the formula for calculation of deduction = Gross Qualifying Amount – Net Qualifying Amount
- The donation should be made in any mode of payment other than cash if it exceeds Rs. 2,000. Donations in kind are not eligible for deduction under this section
Section 80GG: Income Tax Deduction for House Rent Paid
Deduction under this section is available only to those individuals who do not receive benefits by way of HRA(House Rent Allowance) or RFA(Rent Free Accommodation). Deduction u/s 80GG can be claimed to the extent of Rs 5,000 per month for the house rent paid.
The admissible deduction shall be least of the following:
- a. Rs. 5,000 per month
- b. 25% of the adjusted total income*; or
- c. Rent paid less 10% of total income*
*Adjusted Total Income = total income excluding short-term capital gains under section 111A, long term capital gains, income under section 115A and deductions under sections 80C to 80U
Section 80GGA: Income Tax Deduction for Donation towards Scientific Research & Rural Development
Donations for Scientific Research or Rural Development can avail deduction under section 80GGA. Assessee having an income from Business/Profession cannot avail of this benefit. Under this section, the whole amount is allowed as a deduction without any upper limit. However, cash donations of more than Rs. 2,000 are not allowed. Read More about Section 80GGA
Section 80GGB: Income Tax Deduction for donation to Political Parties
Donations made by an Indian company to any political party or an electoral trust shall be eligible for deduction under this section. However, no deduction shall be permissible in respect of cash donations.
Section 80GGC: Income Tax Deduction in respect of contributions given by any person to Political Parties
Any person other than an Indian Company can avail deduction under section 80GGC of the total amount paid to a political party or electoral trust, except the cash donations. However, local authorities and every artificial judicial (wholly or partly funded by the government) person cannot claim a deduction under this section.
Section 80RRB: Income Tax Deduction for Royalty on Patents
A resident of India and an individual patentee (true and first inventor of the invention, including co-patentee) can claim a deduction under section 80RRB in respect of patents registered on or after 01.04.2003. The deduction amount shall be the lower of:
- 100% of Royalty Income from patent
- Rs. 3,00,000
For claiming the benefit under this section patent must be registered under the Patents Act 1970. Read More about Section 80RRB
Section 80QQB: Income Tax Deductions for Royalty Income of Authors
An author (Resident of India or resident but not ordinarily resident in India), including the joint author of a book, can claim a deduction under Sec 80QQB. The deduction amount shall be as follows:
a. In the case of lump sum payment – Total amount of royalty income subject to a maximum of Rs. 3,00,000.
b. In other cases – Total amount of such income subject to a maximum of 15% of the value of books sold during the previous year.
Section 80U: Income Tax Deduction for Disabled Individuals
resident individual certified by the medical authority or a government doctor to be a person with a disability (having a disability of 40% or more) can claim a deduction of Rs. 75,000 under this section. In the case of a person with a severe disability (having a disability of 80% or more ), the quantum of deduction allowed is Rs. 1,25,000. It is a fixed deduction and is not based on actual expenses.
Section 80TTA: Deduction in respect of interest on deposits in Savings Account
Section 80TTA allows deduction in respect of interest income on deposits in Savings Bank Accounts of Banks, Co-Operatives Banks or Post Office. The quantum of deduction allowed under this section is Rs. 10,000 or the actual interest earned, whichever is lower. Both individual and HUF can avail this deduction (Other than Resident Senior Citizen). This deduction is not available on interest income from fixed deposits
Section 80TTB: Deduction in respect of interest from deposits held by Senior Citizens
Section 80TTB allows a deduction upto Rs 50,000 in respect of interest income from deposits held by resident senior citizens (age 60 years or more) with a banking company, a post office, cooperative, society engaged in the banking business etc. Consequently, the limit of tds deduction u/s 194A for senior citizens has been raised to Rs. 50,000. However, no deduction under section 80TTA shall be allowed in these cases. Note that the senior citizen aged 75 years and above, earning only pension and interest income, is exempted from ITR filing as tax shall be deducted at source by the banks.
